The Ranking Report template is an invaluable tool with regards to Business Intelligence Reporting. Within the prompt page of these applications, end-users can:
- Select the number of records they wish returned
- Select the order in which they are returned
- Control the dimension of the report. A dimension is the field used to measure ranking. For instance, if a report was designed to display the top ten salespeople by sales, the dimension would be sales.
- Control the field by which the report will be sorted
Within the output page, end-users will:
- Be shown a numeric list counting the number of records displayed
- A dynamic column that will show the dimension field’s values
- Have a pie graph that shows each dimensions percentage of total graphically
- Have the ability to re-order any column, thus redrawing the data graph
Runtime Walkthrough
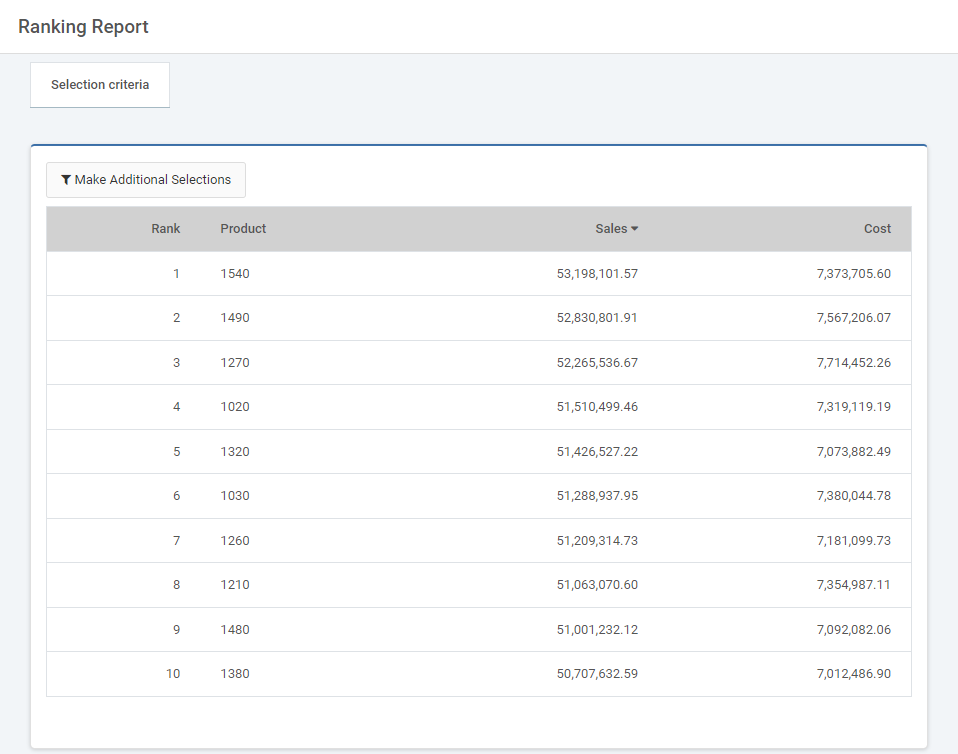
To begin with, the user must select whether to display the top or bottom records, followed by how many records to display. The third option requires the user to select a dimension. In our example, we will be displaying the top ten teams by home runs. Therefore, our dimension will be team name. The Based on Measure option requires the user to select the measure used to determine ranking. In our example, the measure will be home runs. The last option is to select running this report to HTML or Excel. Once done, click run report.
This brings us to the report. We can see the top ten teams in descending order, based on Home Runs. At the bottom of the page is the graph, which has changed to display the top ton records as well. Note that in our application there are five fields with arrows next to their names. These fields are sortable, however sorting on them will change the application to use that field as the measure for ranking. This is reflect in our graph as well. Finally, end-users can change the options they applied in creating the graph by clicking the ‘Make Additional Selections’ button.
Features that Apply to All m-Power Templates
Features that Apply to the Ranking Report Template
All Templates Features
m-Power templates allow you to retrieve rows of data from one or more database tables or database views. Utilizing SQL statements, m-Power connects to your database and allows you to access the data via a web application.
Back To Diagram
Ad Hoc Template Specific:
m-Power templates allow the end user to sort the data fetched from the database. Ascending or descending order can be controlled from the table heading by clicking the up or down arrows. To turn this feature on or off, access the application properties and select Yes or No for the advancedSort property.
Back To Diagram
Format Numeric Data:
m-Power templates allow developers to easily modify the numeric format of fields to better suit your needs, directly from the interface. An example of this can be the use of a comma at the thousand decimal point: (2,000) or the inclusion of decimal digits: (2,000.00) From the application menu, click Field Settings. For numeric fields you will see a Numeric Field Format column, use the drop down to select the numeric format you need.
Back To Diagram
Filter Via Record Selections:
Create hard-coded or user interactive filters based on specific criteria from your data. This feature allows users to filter the data to display only those records that match the selection criteria. Several options are available to create the relationship of the search, including “equal to, not equal to, is in the list, is in the range” and many more. Learn more.
Back To Diagram
Add Multi-Tenant Security:
m-Power applications can be secured to allow different users to access the same application, but see different results, based on the user login credentials. One example of this can be a report that contains records of customers for all the States in the USA, but the user will only work with the customers in his/her home State, via row level security m-Power can filter and display only the customers that the user is allowed to see. This technique allows you to fully implement scalable security solutions. Learn more.
Back To Diagram
Override/Customizable Error Messages:
All m-Power templates allow you to modify the default error messages. Most error messages are generic in describing the issue, maybe you need your users to see a more personalized or informative error message. From the application properties developers can change the error message without having to open the code source of the application. Learn more.
Back To Diagram
Add Drop-Down List or Lookup List to Text Input Fields:
Add a drop down list or lookup window to your application using m-Painter. These features will allow users to input data by selecting it from a list or lookup windows. This enhances the user experience, simplifies their tasks, and allow for less errors on data input. Learn more about Lookup Windows. Learn more about Dropdowns.
Back To Diagram
Add Calendar Widget to Date Inputs:
Using m-Painter developers can add a calendar picker next to a date input field. The date format in the calendar picker can be modified to match the format in the database. This feature will save users time and it will ensure that the date format entered is consistent with the database. Adding a calendar picker will make your application look and feel more professional. Learn more.
Back To Diagram
Call External Object Programs:
m-Power can handle your back-end business code too! The use of External Objects allows m-Power to tie into your custom coding easily, whether it is Java, SQL, or RPG. Learn more.
Back To Diagram
Saved Searches:
For end users running applications, there is a feature that allows them to save the search and come back to it later, saving them time and making it more efficient by saving multiple searches and switching between them with just a click. These searches can be found on the right upper corner of the running application by clicking Options then Saved Searches. Learn more.
Back To Diagram
Customize HTML with m-Painter:
m-Power ships with its own HTML editor. This tool, called m-Painter, allows you to modify the HTML code in a very easy way by using a WYSIWYG (What You See Is What You Get) editor, where all the graphical modifications are instantly visible. For the advance developers, there is a text editor mode too. You can access the HTML editor by clicking Presentation on the Application Menu. Learn more.
Back To Diagram
Control DB Join Type:
When joining tables you can set the join type of the application to be Left Outer Join or Inner Join. An inner join specifies that only records in the primary table with matching records in the secondary table will be displayed.
Back To Diagram
Add Row-Level Logical Fields:
m-Power allows you to create a logical field at the database level that is available to all applications. The options are Substring, Concatenation, or UDF (User Defined Function). By creating these files at the dictionary level, they are reusable across the entire dictionary, saving the developer time! Learn more.
Back To Diagram
Tablet & Mobile Output:
m-Power allows developers to create applications specifically for PC browser, Tablet, and Smartphone devices. For the user, this means that they can access the same report on their PC, tablet, and smartphone and see a completely different output on each that has been tailor-made for their device. For the developer, it means that they can create and maintain one single application that will create the proper output formats automatically. Learn more.
Back To Diagram
SmartLinks:
SmartLinks allow developers to easily link one application (Inquiry, Report, or Maintenance) to any other application, passing key data automatically. An example of this can be an Inquiry or a Report that links to a maintainer to update only an specific record and then redirect back to the list of records. By SmartLinking applications m-Power makes it easy to link applications together to create smooth navigation between web applications. Learn more.
Back To Diagram
Ranking Report Features
As the name suggests, Ranking Reports are excellent at displaying data based on ranking. Take for example a Ranking Report built over salesperson data. A ranking report could easily be used to determine which salespeople has the top sales or the top commissions. Alternatively, at runtime, end-users can choose to display the bottom ranking, rather than the top.
Back To Diagram
Advanced Graphing:
By default, a Ranking Report includes a 3D pie chart graph. This graph is dependent on end-users runtime selections, allowing the graph’s data set to change as needed. Developers can customize this graph via m-Painter, for instance changing default colors and graph type.
Back To Diagram
Runtime Value Prompt Record Selections:
Instead of only supporting hard coding a value within a record selection, reports also support runtime value prompts. Runtime value prompts allow users to input a value at runtime, creating a dynamic data selection.
Back To Diagram
Multiple Output Options:
Ranking Reports have a variety of output options. You can choose whether to run the report to the browser, to Excel, or to email. Additionally, these options can be specified by the developer, or selected by the user at runtime.
Back To Diagram
Messaging and Scheduled Task Integration:
This template can be used in combination with the Scheduled and Messaging Task utility. This allows you to schedule running Ranking Reports at off-peak times to avoid slowing down your system. You can also use the utility to email scheduled Ranking Reports, either in the body of an email, or as an attachment.
Back To Diagram
Override-able SQL Statement:
The Ranking Report template allows developers to override the SQL statement. This can be done by accessing the application properties and clicking on the SQL Statement tab. Learn more.
Back To Diagram
Template Notes
Application Settings
Program Name: This will be the application’s number. By default m-Power uses the letter R (Report) followed by a five digits number. This number is automatically incremented by 10, but can be manually changed.
Note: The number must be unique in the Data Dictionary.
Select Only Matching Records: When joining to other tables, you have the option to create a Left Outer Join or and Inner Join. Selecting Yes (inner join) will include only matching records from the joined table. A simple example of this could be a Sales History table that links to a Product Master table. Now imagine some products have been discontinued and subsequently removed from the Product Master table. With an outer join, the discontinued products will still be reported. However, with an inner join, records without matching records in the product master will be omitted from the result set.
Summary or Detail Report: Select whether to display detail (by default), or to not display detail, by choosing summary.
Template: You can select a template by scrolling through the available templates. The templates define the general layout and functionality of the resulting application. This section will list all the available report templates; you will see a small screenshot of what that template looks like at runtime. Learn more about templates.
Data Selection
Here you will see/modify the primary table you have selected for your application. Here you can create or modify joins to other tables as well.
Sequencing
Here you can select the field that your application will sequence by; you can have multiple sequence fields. You can re-order the sequences to fit your application’s needs. In Ranking Reports, the subtotaling and new page options can be ignored.
Note: Only fields that are set as sequence fields are available as Dimensions at runtime. For instance, imagine you have an application in which you want to view the top ten records by salesperson. In this situation, the salesperson field would need to be a Dimension, and therefore also a sequence field.
Learn more about general sequencing.
Field Settings
Here you will find the settings for all the fields in the application. The options are:
Note: Deleting a field will remove the field from the application only, the table will be unchanged.
Field Name: This is the same name the field has in the table.
Table: The name of the table where that field exists.
Field Description: This is the text that will appear in the column header for that field, you can modify this field to suit your needs. This field will populate with the field description from the table by default, but it can be customized at the application level.
Display: A radio button allows developers to display or hide the field from the output page. There may be situations where a field is needed for calculation purposes, but the field does not need to be displayed at runtime. Note: Non-sequence fields that are set to display will appear in the ‘Based on Measure’ dropdown, and be available for ranking. If you do not want a field to be available for ranking, set this field to non-display.
Length: Here you can modify the length of the field. m-Power will only allow developers to shorten the length of the field, shortening a fields length will truncate its data. For example, if a field is 10 alpha and it is changed to 5 alpha, now only the first 5 characters will be displayed. The same principle applies to a numeric field, if a numeric field is 8 digits long; changing it to 4 digits long will only display the first 4 digits, and leave out the rest of digits.
Decimals: For numeric fields, you can modify the amount of decimal digits. A numeric field will have the option of changing its decimal length, alpha fields does not have a decimal option, developers can use this as an indicator to check if a field is a numeric or character type.
Numeric Format Code: For numeric fields, you can modify the way the numbers will display, this includes displaying decimals or not, how to display negative numbers, etc. Multiple formats are built in for developers to use, shall you need a different format code, m-Power allows developers to create their own User Defined Format codes; these codes will add logic for common types of fields such as: Currency, Time, or Dates. Accessing the User Defined Format Codes from the Admin section will also allow developers to modify current codes. Learn more.
Note: Do not confuse the User Defined Format Code with the User Defined Functions (UDF). The latter is a feature that allows developers to create or incorporate programing functions into m-Power. Learn more about UDFs.
User def: This feature has being deprecated
Record Selections
Record Selections can be created over fields from both primary as well as secondary tables. These are the options:
Relation: A drop down allows you to select a relationship for the filter.
Value: This is the value to compare against. The options are:
Constant Value: A constant value allows you to hard-code any given value into a selection. This value cannot be modified by the end-user at run–time.
Application Field Value: Developers have the option of comparing a value from one field to a value from another field within the same record.
Runtime Value Prompt: This option will create an input within the HTML that will allow users to input a value for the record selection at runtime. Runtime value prompts allow users select data specific to their individual needs.
And/Or: When creating multiple record selections, you have the option to set them as “and” or “or” Example: selection A “and” selection B will display only records that match both selections. Selection A “or” selection B will display records that match one or both selections. Learn more.
Calculations
Calculations are a very powerful feature of m-Power; with calculations, developers can create logical fields that will apply to the current application only. This can be used to include SQL code in a field, such as cast a numeric field as character, create date conversions, inserting the current date and time, and much more. Learn more.
External Objects
This feature allows developers to connect m-Power application with their current business logic, or to extend m-Power capabilities by allowing developers to write their own Java, RPG, or SQL programs, and integrating these programs into the applications. m-Power utilizes “locations” to connect the external objects, these locations vary depending on what the external object does and when it should be executed. The following locations are supported in this template: Learn more
*JREADRECRD This location will call the external object after each record is processed.
*ADVRECSEC This location has been deprecated. Learn more about Row Level security.
*STRSEARCH This location has been deprecated.
*STRUPBDFT This location has been deprecated.
*SELECT This location has been deprecated. Learn more about creating dropdown lists using m-Painter.
*RUNVALID This location is used to validate prompt inputs.
SmartLinks
SmartLinks allow developers to easily link one application (Retrieval, Report, or Maintenance) to any other application, passing key data automatically. The benefits of this are many, including: creating applications that will allow developers to link a Retrieval to a Maintainer in order to update an specific record passing key parameters automatically. Create a Hover-Over window; create a popup dialog, and many more. By, passing parameters automatically when creating a link in m-Painter, SmartLinks save the developer time by simplifying the process. Learn more.
Note: After performing any changes in the above sections, the application must be recompiled for the changes to load. If the changes are to be displayed at runtime, then the Presentation Layer code (HTML) must be overwritten when recompiling the application.
Template In-Action
Application Properties
When accessing the Application Properties, a window will slide open with several tabs; let’s go through each of the tabs:
