Overview
This document will explain how to create, register, and call a sample External Object written in SQL. Recall from basic training that the purpose of an External Object is to call your back-end business logic directly through an m-Power web application. In this case, the purpose of this External Object will automatically delete all detail lines from an Order Detail table as soon as the parent record is deleted in the Order Header file. If you would like to see similar documentation of this External Objects written in different languages, please click one of the following links:
Creating an SQL External Object
Prior to creating an External Object, you must first decide what the purpose of the object will be. As discussed above, the purpose of this External Object will automatically delete all records from an Order Detail table as soon as the parent record is deleted from the Order Header table. The source code needed to create this object can be found here.
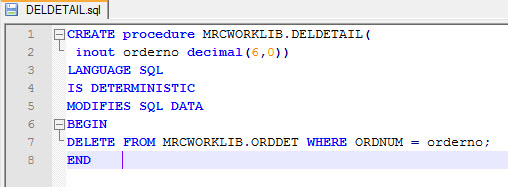
As you will notice from the code, this object receives a single parameter (Order #), then deletes all records from the Order Detail file with a matching Order #.
Copy and paste the attached SQL code into your favorite SQL command line editor and run the statement. This will create an SQL procedure on your database. The next step will be to register the procedure into your m-Power environment.
Registering your SQL External Object to m-Power
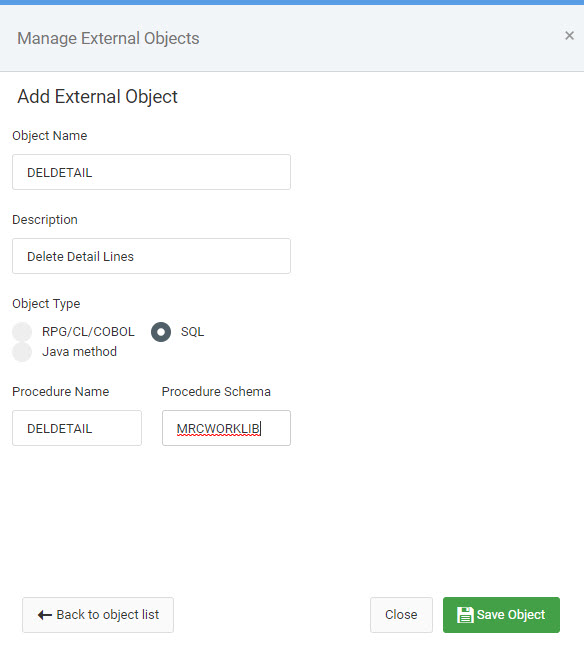
Open the m-Power interface and click on “Admin” in the header bar. From here, click the “External Objects” button. Then, click “Manage” and finally click the “Create New External Object” button. Enter the SQL object name as referenced within the source code, then enter a description that will only be visible by fellow developers. Next, select “SQL” for the Object type. Lastly, re-enter the Program name and specify the correct library/schema. When complete, your screen should resemble the screenshot listed below:
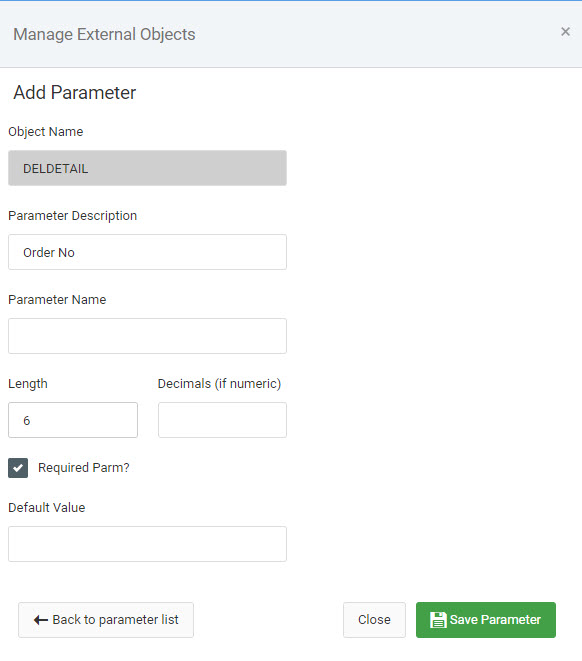
Once the main program is registered, you will next need to register the necessary parameters. Find the program you just registered and click the “View Parms” button. Click the “Create New Parameter” button, then enter in a Parameter Description that will only be visible to fellow developers. Lastly, enter in the parameter length as specified in your SQL object. Remember, to map this parameter to your application, you will need a field that has matching attributes. Mark “Yes” for “Required Field”. Then press “Save”. When complete, your screen should resemble the screenshot listed below:
Calling your SQL External Object within m-Power
Now that you have successfully created your External Object and registered it to m-Power, the final step to complete is calling your object at the application level. Since the purpose of this application is to delete records from the child table when the matching record is removed from the parent table, the ideal way to call this object would be from a Maintenance application. The idea here is to let the Maintenance application delete the one parent record, then call your object to delete all necessary child records.
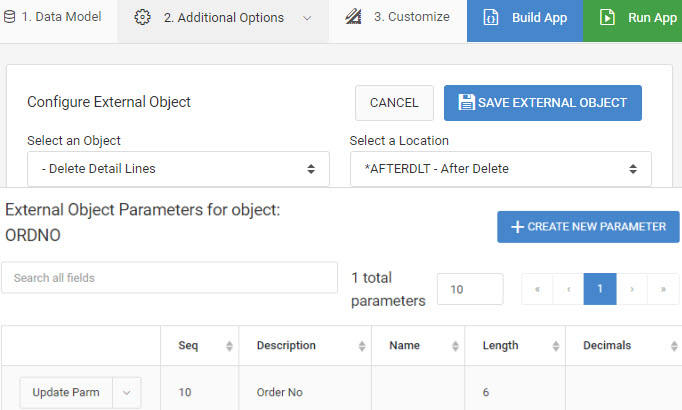
After selecting all necessary fields for your maintenance application, click the “External Objects” icon within the “2. Additional Options” tab. Select the newly created object from the “Select an object” drop-down. Next, select the After Delete (*AFTERDEL) location from the “Select a Location” drop-down. The reason for using the After Delete location is because we only want the object to be called when a record is deleted from your main application. If a record is added or updated, your application will not be run. Finally, map the correct parameter for the Order #. When complete, your screen should resemble the screenshot listed below:
Compile and run your application. When you delete a record from your Maintenance application, any records that match in your child table (based on the parameter passed to the External Object) will also be deleted.
Notes
- When an External Object is called, your Web application gives all control to the object. Only after the object has completed will control return back to the end-user. For example, if an External Object takes 20 seconds to run, as soon as the user clicks “Accept” to initiate the Object, the user’s cursor will turn into a “Waiting” state until the object has finished running. Once completed, the program will finish running.
- External Objects are run in order, based on the External Object locations. External objects called at the same location will be called in the order they were defined to the application. More information about External Object locations can be found here.
- When using this guide to create your own SQL External Object be sure to replace all references of MRCWORKLIB to your library/schema and DELDETAIL to your object’s name.
